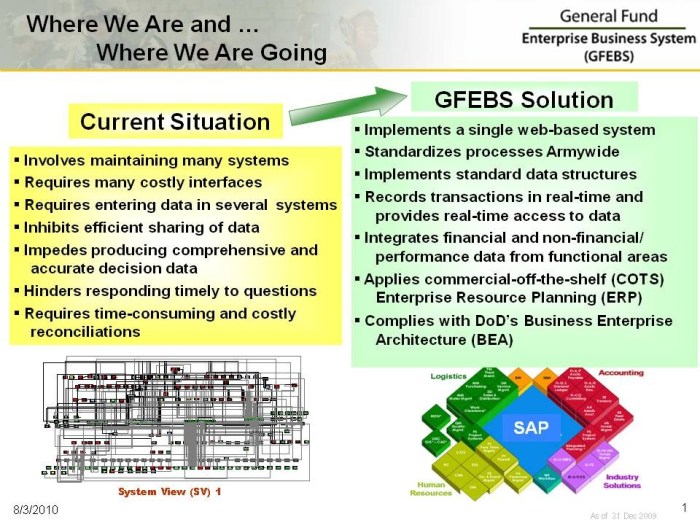
In order to complete your transaction in GFEBS, understanding the process and adhering to the guidelines is essential. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the steps involved, security measures, and best practices to ensure seamless transaction completion.
GFEBS (Global Financial Electronic Banking System) is a robust platform designed to facilitate secure and efficient financial transactions. To ensure the integrity and accuracy of these transactions, GFEBS employs a rigorous verification process, utilizes advanced data management practices, and complies with stringent security standards.
Transaction Verification
Transaction verification in GFEBS ensures the integrity and validity of financial transactions. It involves verifying the authenticity of the transaction parties, the accuracy of the transaction details, and compliance with applicable regulations.
Methods of Transaction Verification, In order to complete your transaction in gfebs
- Digital signatures and encryption
- Two-factor authentication
- Biometric authentication
- Transaction risk analysis
Security Measures for Verification
- Data encryption
- Secure network protocols
- Access controls and role-based permissions
- Audit trails and transaction logs
Transaction Completion Procedures: In Order To Complete Your Transaction In Gfebs
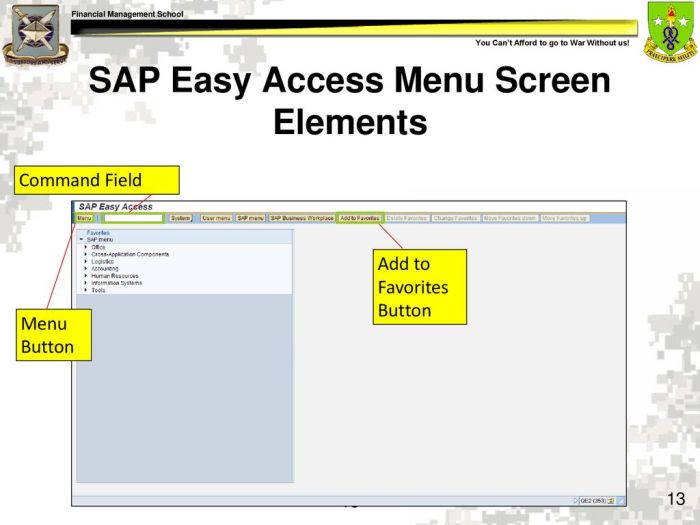
Transaction completion in GFEBS involves a series of steps and requires collaboration among various parties.
Steps Involved
- Initiation of the transaction
- Verification of the transaction details
- Authorization and approval
- Execution of the transaction
- Settlement and finalization
Roles and Responsibilities
- Transaction initiator
- Transaction approver
- Transaction executor
- Transaction settlement agent
| Step | Description | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Creation and submission of the transaction request | Transaction initiator |
| Verification | Validation of transaction details and authorization | Transaction approver |
| Execution | Carrying out the transaction | Transaction executor |
| Settlement | Transfer of funds and finalization of the transaction | Transaction settlement agent |
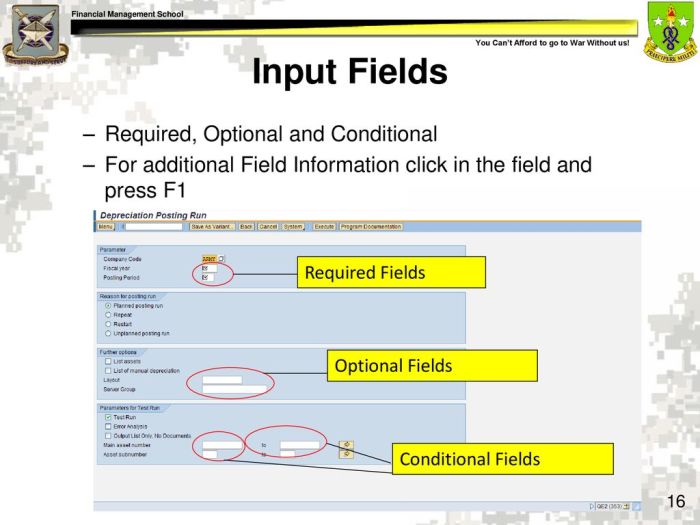
Error Handling and Resolution
Errors during transaction completion can arise due to various reasons. Effective error handling and resolution mechanisms are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the GFEBS system.
Common Errors
- Invalid transaction data
- Insufficient funds
- Authorization failures
- System outages
Troubleshooting and Resolution
- Identifying the error source and cause
- Implementing corrective actions
- Reversing or adjusting the transaction as necessary
- Documenting and reporting the error
Best Practices for Error Management
- Establish clear error codes and descriptions
- Provide user-friendly error messages
- Implement automated error detection and handling mechanisms
- Regularly monitor and analyze error logs
System Integration and Data Management
System integration and data management are critical aspects of ensuring seamless transaction completion in GFEBS.
Importance of System Integration
- Enables data exchange between GFEBS and other systems
- Facilitates automated transaction processing
- Improves efficiency and reduces errors
Data Management Practices
- Data standardization and validation
- Data encryption and security
- Data backup and recovery
- Data auditing and compliance

Security and Compliance

Robust security measures and compliance with industry standards are essential for protecting transactions in GFEBS.
Security Measures
- Encryption and data protection
- Access controls and authentication
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems
- Regular security audits and penetration testing
Compliance Requirements
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
| Standard | Scope | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| PCI DSS | Payment card data security | Data encryption, access controls, intrusion detection |
| GDPR | Data protection and privacy | Data subject rights, data breach notification, consent |
| SOX | Financial reporting and internal controls | Internal control over financial reporting, external audit |
User Experience and Interface Design
User experience and interface design play a crucial role in facilitating efficient and user-friendly transaction completion.
Design Principles
- Clarity and simplicity
- Intuitive navigation
- Error prevention and feedback
- Accessibility and inclusivity
Feedback Mechanisms
- User surveys and feedback forms
- Error reporting and analytics
- User testing and usability studies

Transaction Monitoring and Reporting
Transaction monitoring and reporting are essential for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of GFEBS transactions.
Monitoring Methods
- Real-time transaction monitoring
- Transaction pattern analysis
- Fraud detection algorithms
Reporting Mechanisms
- Transaction reports
- Audit trails
- Regulatory compliance reports
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Transaction volume | Number of transactions processed |
| Average transaction value | Average value of transactions |
| Fraud detection rate | Percentage of transactions identified as fraudulent |
| Compliance violations | Number of transactions violating compliance regulations |
Top FAQs
What are the key steps involved in completing a transaction in GFEBS?
The key steps include transaction verification, data entry, authorization, and confirmation.
How does GFEBS ensure the security of transactions?
GFEBS employs encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits to protect transactions from unauthorized access and fraud.
What is the role of data management in GFEBS?
Data management ensures the accuracy, integrity, and availability of transaction data, facilitating efficient processing and reporting.