Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of cell division with our quiz on meiosis and mitosis. From the fundamentals to the intricate details, this quiz will illuminate the processes that shape the very fabric of life.
Delve into the intricacies of mitosis, the process responsible for growth and repair, and unravel the complexities of meiosis, the driving force behind sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. Prepare to test your knowledge and deepen your understanding of these fascinating biological phenomena.
Introduction to Mitosis and Meiosis
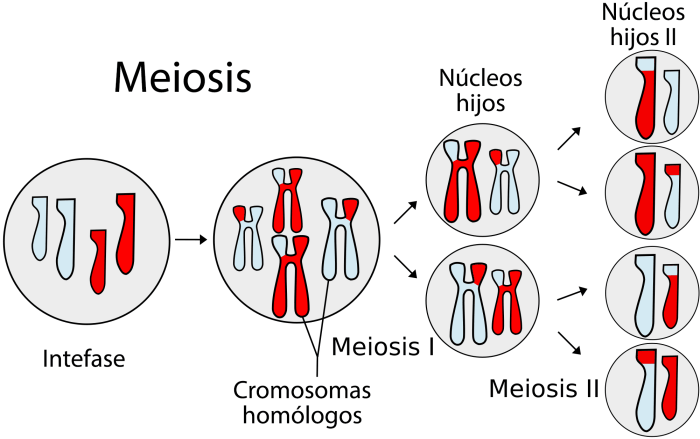
Mitosis and meiosis are two fundamental cell division processes that play crucial roles in the life cycle of organisms. While both processes involve the division of a parent cell into two or more daughter cells, they differ in their specific mechanisms and outcomes.
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. It is primarily responsible for growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in many organisms. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells (gametes) and results in four genetically distinct daughter cells.
Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures the production of haploid gametes (eggs and sperm) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
The following table summarizes the key differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Growth, tissue repair, asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| Number of daughter cells | Two | Four |
| Genetic similarity to parent cell | Identical | Distinct |
| Chromosome number in daughter cells | Same as parent cell (diploid) | Half of parent cell (haploid) |
| Number of cell divisions | One | Two (meiosis I and meiosis II) |
| Crossing over | No | Yes |
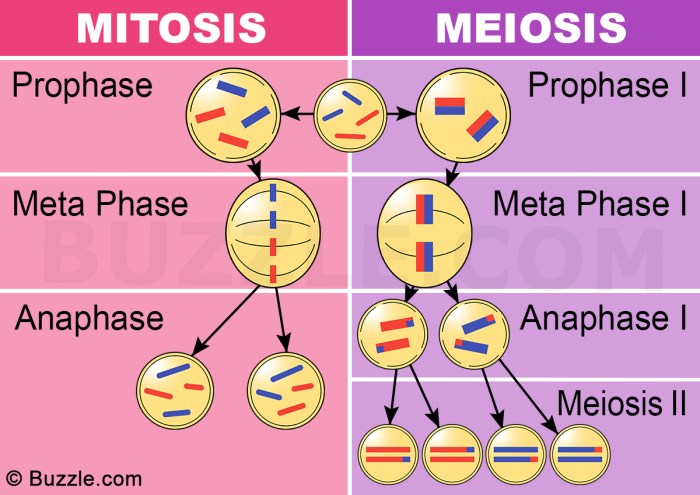
Phases of Mitosis
Mitosis, a type of cell division, occurs in somatic cells (body cells) and is crucial for growth, development, and tissue repair. It involves four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase
During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle forms. The spindle fibers, composed of microtubules, attach to the chromosomes’ centromeres.
Metaphase
In metaphase, the chromosomes align along the metaphase plate, an imaginary line at the equator of the cell. The spindle fibers ensure that each chromosome is attached to spindle fibers from opposite poles of the cell.
Anaphase
Anaphase marks the separation of sister chromatids, which are identical copies of each chromosome. The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase, Quiz on meiosis and mitosis
In telophase, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell. The spindle fibers disappear, and two new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes. The cytoplasm divides through cytokinesis, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Phases of Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in the reproductive organs of sexually reproducing organisms. It produces gametes, or sex cells, such as eggs and sperm. Meiosis is a complex process that occurs in two phases: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Meiosis I
Meiosis I is the first phase of meiosis. During this phase, the cell’s chromosomes are duplicated and then paired up with their homologous chromosomes. The homologous chromosomes then exchange genetic material through a process called crossing-over. After crossing-over, the homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Meiosis II
Meiosis II is the second phase of meiosis. During this phase, the chromosomes from each homologous pair separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. This results in the formation of four haploid daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Similarities and Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
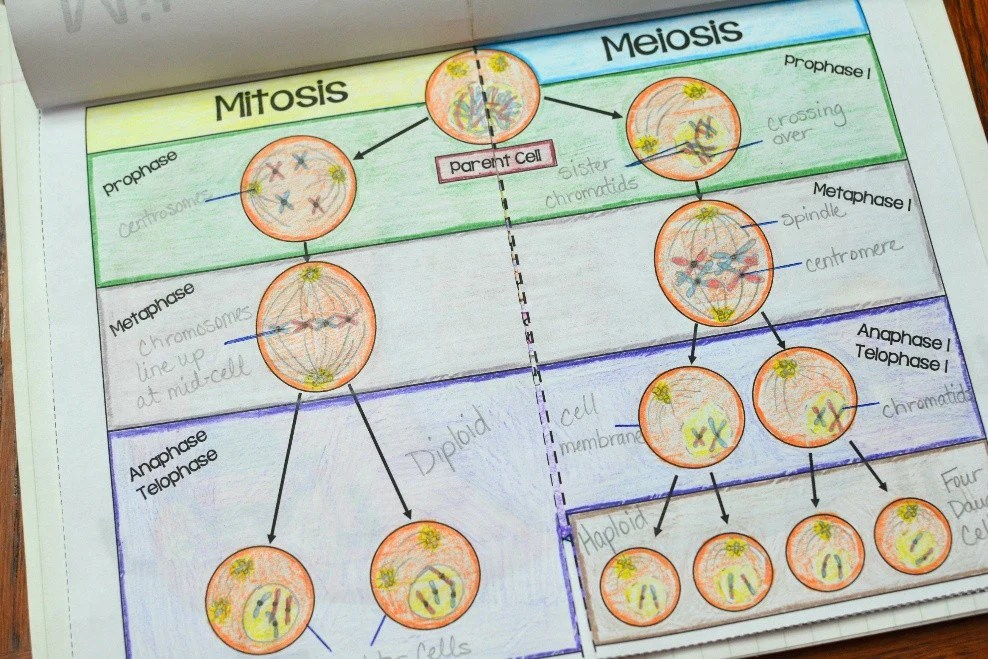
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct cell division processes that occur in eukaryotic cells. While they share some similarities, they also have key differences in terms of the number of divisions, chromosome number, genetic variation, and purpose.
Comparison Table
The following table summarizes the similarities and differences between mitosis and meiosis:
| Category | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of divisions | One | Two |
| Chromosome number | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
| Genetic variation | No | Yes |
| Purpose | Growth, repair, and asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
Examples of Mitosis and Meiosis: Quiz On Meiosis And Mitosis
Mitosis and meiosis are essential processes in the life cycles of all organisms. Let’s explore specific examples to understand their occurrence and significance.
If you’re looking for a break from studying the intricacies of meiosis and mitosis, why not take a virtual tour of the nine tourist regions of West Virginia ? From the rolling hills of the Potomac Highlands to the whitewater rapids of the New River Gorge, the Mountain State offers a diverse range of natural beauty that will rejuvenate your mind and prepare you to tackle those complex cell division processes with renewed vigor.
Mitosis
Mitosis occurs in somatic cells (non-reproductive cells) and is responsible for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
- Growth:Mitosis allows organisms to increase in size and complexity by producing new cells.
- Repair:Mitosis replaces damaged or lost cells, ensuring the proper functioning of tissues and organs.
- Asexual reproduction:In some organisms, such as bacteria and certain plants, mitosis is the primary means of reproduction, creating genetically identical offspring.
Meiosis
Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells (gametes) and is responsible for producing gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Sexual reproduction:Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction, as it creates gametes (eggs and sperm) with a unique combination of genetic material.
- Genetic diversity:The process of meiosis involves genetic recombination, which shuffles the genetic material and creates gametes with new combinations of genes.
- Gamete formation:Meiosis produces gametes that are haploid (n), containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, which is diploid (2n).
Importance of Mitosis and Meiosis
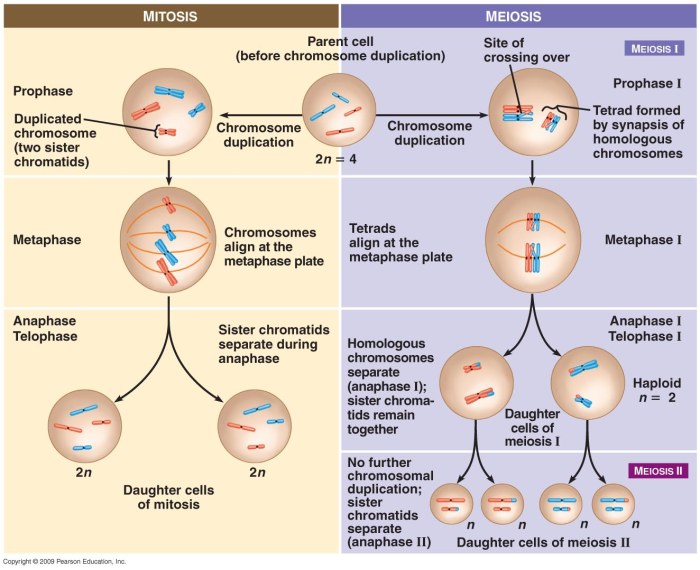
Mitosis and meiosis are essential processes for all living organisms. They play crucial roles in growth, repair, and reproduction.
Importance of Mitosis
Mitosis is responsible for cell growth and repair. It ensures that each new cell receives a complete set of genetic material, allowing the organism to maintain its genetic integrity. Mitosis is also essential for the repair of damaged tissues, as it allows the body to replace damaged cells with new, healthy ones.
Importance of Meiosis
Meiosis is responsible for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. It produces gametes (eggs and sperm) that contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells. When gametes fuse during fertilization, they combine their genetic material to create a new individual with a unique combination of traits.
Meiosis also ensures that each new individual has a different genetic makeup from its parents, which is essential for the survival and evolution of species.
Quiz on Mitosis and Meiosis
Test your knowledge of mitosis and meiosis with this comprehensive quiz. From multiple-choice questions to short answers and true/false statements, this quiz will challenge your understanding of these fundamental cell division processes.
The quiz covers various aspects of mitosis and meiosis, including their stages, similarities, and differences. It also explores the significance of these processes in biological systems.
Multiple Choice
- Which of the following is the correct sequence of stages in mitosis?
- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
- Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Interphase, Telophase
- Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of meiosis?
- It produces four daughter cells.
- It involves crossing over.
- It occurs in somatic cells.
- Which of the following is a similarity between mitosis and meiosis?
- Both involve DNA replication.
- Both produce genetically identical daughter cells.
- Both occur in all eukaryotic cells.
Short Answer
- Describe the role of the spindle fibers in mitosis.
- Explain the difference between homologous and non-homologous chromosomes.
- Discuss the importance of meiosis in sexual reproduction.
True/False
- Mitosis is used for growth and repair of tissues.
- Meiosis produces haploid daughter cells.
- Interphase is not a stage of mitosis.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the key difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.
Which phase of mitosis is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the equator of the cell?
Metaphase
How many rounds of division occur in meiosis?
Two
What is the role of crossing over in meiosis?
To exchange genetic material between homologous chromosomes, increasing genetic diversity.